Urology FAQs & Patient Education
What is Urology?
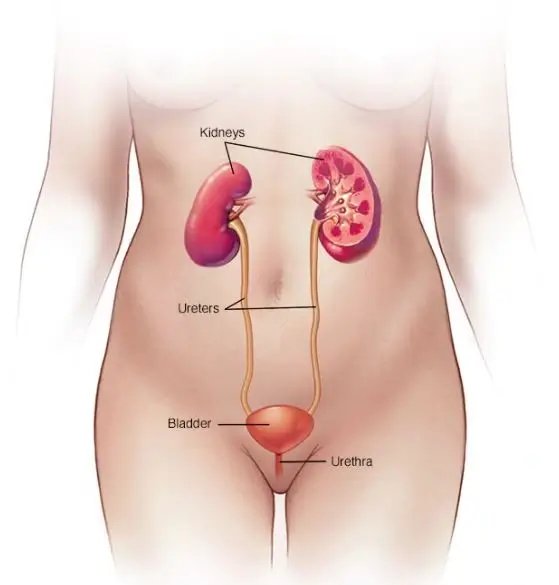
Urology is the surgical specialty which essentially focuses on the disorders or diseases associated with the urinary tracts of males and females, and the male reproductive system. Medical professionals who specialize in this field are called urologists and are trained to effectively diagnose, treat, and manage patients suffering from urological disorders. The various organs covered by urology include the kidneys, ureters, urinary bladder, urethra, and the male reproductive organs namely; the, epididymis, vas deferens, seminal vesicles, prostate and penis.
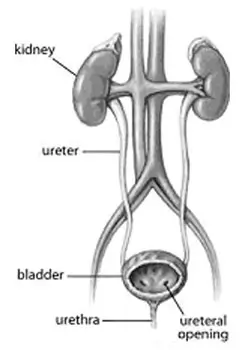
Urology involves the management of non-surgical medical problems such as urinary tract infections and benign prostatic hyperplasia, as well as complicated surgical problems such as the surgical management of different types of cancers and correction of congenital defects. Moreover, it is closely related to the other medical fields including Oncology, Nephrology, Gynecology, Gastroenterology, and Endocrinology. Urology is a discipline that combines the study of different organs and physiological systems and has different sub-fields.
What is Andrology?
This specialty includes the treatment of physical conditions affecting the male genitalia, such as undescended testes, diseases affecting male fertility and sexual functions. Health conditions such as high blood pressure, heart disease, and kidney failure can all reduce sexual function. So Andrologists work together with caregivers in those fields. They also help in retrieving sperms for in-vitro fertilization and various assisted reproductive techniques. They perform vasectomies as means of male contraception. Also, they restore the reproductive potential in males with best possible medicines and surgeries if required.
Since male sexuality is largely controlled by hormones, andrology overlaps with endocrinology. Surgery in this field includes fertilization procedures, vasectomy reversals and the implantation of penile prostheses.
Dr Praveen Pandey is one of the best Andrologist in Lucknow. He has rich experience in dealing with disorders of the male sexual function and reproductive system. He works in close association with leading IVF centers of Lucknow to solve issues related to Male infertility.
What are the symptoms of kidney stones?
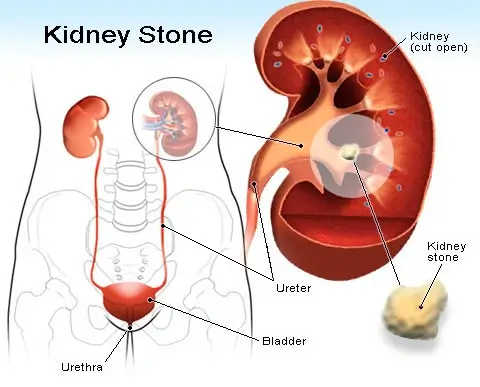
Kidney stones (renal lithiasis, nephrolithiasis) are hard deposits made of minerals and salts that form inside your kidneys. Kidney stones have many causes and can affect any part of your urinary tract — from your kidneys to your bladder. Often, stones form when the urine becomes concentrated, allowing minerals to crystallize and stick together.
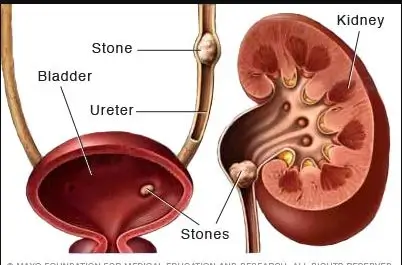
Passing kidney stones can be quite painful, but the stones usually cause no permanent damage if they're recognized in a timely fashion. Depending on your situation, you may need nothing more than to take pain medication and drink lots of water to pass a kidney stone. In other instances — for example, if stones become lodged in the urinary tract, are associated with a urinary infection or cause complications — surgery may be needed.
Symptoms
A kidney stone may not cause symptoms until it moves around within your kidney or passes into your ureter — the tube connecting the kidney and bladder. At that point, you may experience these signs and symptoms:
- Severe pain in the side and back, below the ribs
- Pain that radiates to the lower abdomen and groin
- Pain that comes in waves and fluctuates in intensity
- Pain on urination
- Pink, red or brown urine
- Cloudy or foul-smelling urine
- Nausea and vomiting
- Persistent need to urinate
- Urinating more often than usual
- Fever and chills if an infection is present
- Urinating small amounts
When to see an Urologist?
You may consult an urologist if you have problems such as:
- Urinary tract infection, kidney stones and bladder infections
- Painful urination
- Male infertility problems, such as low sperm count and sperm abnormalities.
- Erectile dysfunction or ejaculatory problems
- Blood in the urine or Hematuria which could be an early sign of a bladder or kidney cancer.
- An increase in PSA levels or a change in PSA, the most sensitive indicator of prostate cancer.
- Any abnormality such as small nodules or irregularities in the prostrate
- Any defect or abnormality of the kidney revealed by your X-ray/ USG/CT Scan.
- A testicular mass or continuous pain in testicles.
- Erections problems and men's health issues.
What causes Kidney Stones?
Factors that could increase the potential risk of developing kidney stones include:
- Your family history
- Kidney stones are usually common in young adults who are above 25 years and even older people.
- Men are more vulnerable to developing kidney stones when compared to women.
- Dehydration.
- People who live in regions which have predominantly warm climates and those who are prone to excessive sweating are at a higher risk than others.
- Consuming food rich in protein, sodium and sugar
- Obesity
- Gastric bypass surgery, inflammatory bowel disease or chronic diarrhea can bring about changes in the digestive process, which could in turn affect the assimilation of calcium and water. This enhances the level of kidney stones in your urine.
- Other medical conditions such as Renal tubular acidosis, Cystinuria, Hyperparathyroidism,
- Urinary tract infections
- Certain medications
What’s the best way to treat Kidney Stones?
The treatment of kidney stones basically depends upon its size, location and composition. Keeping your body hydrated and taking certain medicines can help a small stone pass easily. However, for problem stones, there are certain other treatment options:
- Extracorporeal Shock Wave Lithotripsy or ESWL is a process that makes use of shock (sound) waves to break or disintegrate a large kidney stone into tiny fragments so that it can easily pass out of the body through the urine.
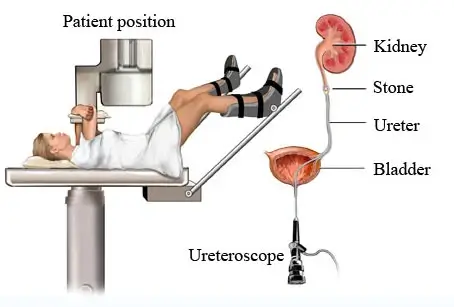
- Ureteroscopic Stone Removal (URS) uses a small telescope with a laser to crush stones stuck in the ureters.
- Percutaneous Nephrolithotomy (PCNL, PNL) is a endoscopic surgical procedure that is used to remove large stones from the kidneys.
- Retrograde IntraRenal Surgery (RIRS) uses a flexible endoscope to enter the kidney through the urethra to crush stones or ablate tumors using a laser
There’s blood in my urine. What could be causing this?
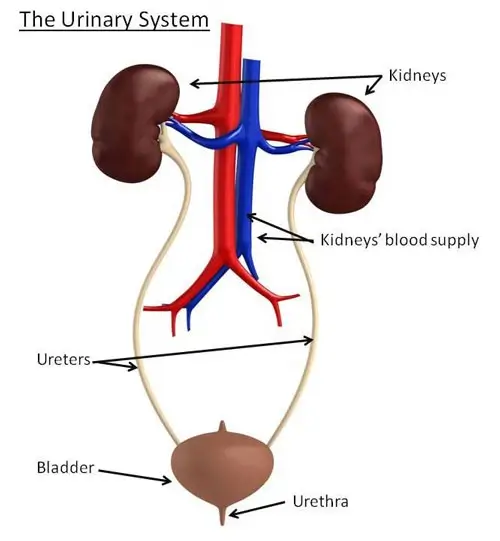
Blood in urine, also known as Hematuria, is in fact a symptom and not a particular condition. Cases of hematuria should be precisely evaluated by the doctor to determine or rule out an underlying cause. Blood in urine can usually come from the kidneys, ureters, bladder or urethra.
Some of the possible causes of blood in urine include:
- Infections in the Bladder or kidney
- Bladder or kidney stones
- Benign prostatic hyperplasia or Enlarged prostate
- Certain kidney diseases, such as glomerulonephritis or inflammation that occurs in the filtering system of the kidneys.
- Prostate cancer
- Certain genetic diseases such as sickle cell anemia and cystic kidney disease.
- Some medications such as aspirin, heparin, cyclophosphamide, and phenazopyridine.
- Tumor in the bladder, kidney, or prostate.
- Injury to the kidney from an accident or sports.
- Performing vigorous exercise.
It’s painful to urinate; what could be the problem?
Dysuria refers to pain, discomfort, or burning sensation when urinating. This symptom is more common in women than in men. However, it is common in older men than young people.
Some of these are the common causes of painful urination:
- Urinary tract infections (UTI) caused due to several factors such as diabetes, advanced age, enlarged prostate, kidney stones, pregnancy and having a urinary catheter in place.
- Vaginal infection
- Sexually transmitted infections such as Genital herpes, Chlamydia and Gonorrhea.
What are the most common procedures Urologists perform?
Most of the procedures do not require any cut or incision on the body of the patient.
The most common procedures which urologists perform in an office setting include:
- Cystoscopy or visual scope inspection of the urethra and bladder and prostate in men
- Removal of stents
- Dilatation of the Urethra
- Urodynamic studies
- Vasectomy or permanent male birth control
- Shock wave Lithotripsy
The common procedures performed in an operating room setting include:
- Transurethral surgeries for benign prostate hypertrophy and bladder tumors
- Removal of kidney stones or ureteral stones
- Removal of the kidney or prostate owing to cancer
- Anti-incontinence surgeries for men and women.
- Placement of penile prostheses.
- Vasectomy reversals
