Urological Prosthetics
Penile Prosthesis
Penile Prosthesis (implants) treat erectile dysfunction (ED) unresponsive to medications, vacuum devices, or injections, and address Peyronie's disease or penile trauma. They restore the ability to achieve erections suitable for intercourse, with high satisfaction rates of 80-95% for modern devices.
Types
Two main categories exist: inflatable (most common in the US) and malleable (semirigid).
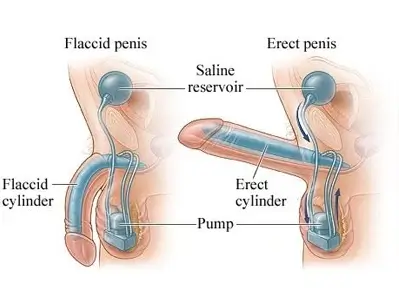
- Inflatable implants feature cylinders in the penis, a scrotal pump, and an abdominal fluid reservoir; manual pumping creates an erection by filling the cylinders.
- Malleable rods keep the penis firm but bendable for positioning, offering simplicity but less natural flaccid appearance.
Procedure
Surgery lasts 45-60 minutes under anesthesia, with a scrotal or penile incision to place components into the corpora cavernosa. Antibiotics reduce infection risk (1-3%), and drains manage fluid; recovery involves 4-6 weeks before use.
Risks and Outcomes
Complications include infection, mechanical failure (5-10% over 10 years), or erosion, but devices last 10-20 years. Implants do not enlarge penis size, enhance sensation, or affect fertility; natural erections cease post-implantation
Testicular Prosthesis
For a variety of reasons, in both children and adults, a testis can be missing or removed. This is where testicular implants come into the picture. This can happen from surgery for cancer, accidental injury, twisting or lack of development of a normal testis.
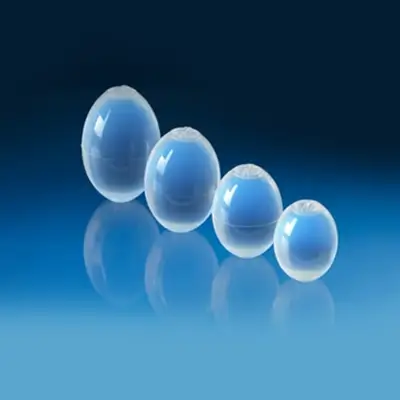
An artificial testis, often called a testis prosthesis(also referred to as “prosthetic testicle” or “testicular implants”), can be implanted to restore the normal appearance of the scrotum and to hopefully restore quality of life.
Testicular implants are pouches that are placed in the scrotum. They are made of solid or gel silicone and have a silicone covering. Some types are coated with polyurethane foam.

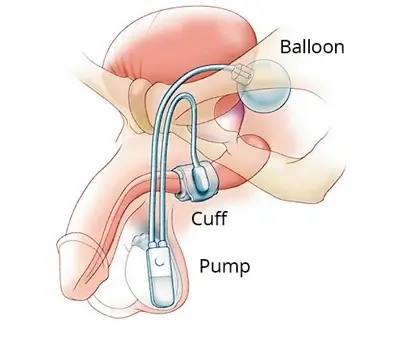
Artificial Urinary Sphincters
An artificial urinary sphincter (AUS) is an implanted device to treat urinary incontinence in men. The AUS is designed to supplement the function of the natural urinary sphincter that restricts urine flow out of the bladder.
Most AUS devices employ an inflatable clamp or collar that is fitted around the urethra to supplement or supplant the function of the natural sphincter. The clamp is inflated automatically and deflated manually by a pump that, depending on the model, is variously placed within the scrotum (for models intended for adult men)